BacLink and
BD EpiCenterTM
and BD PhoenixTM
INTRODUCTION
WHONET is Windows-based database software developed for the management of microbiology laboratory data and the analysis of antimicrobial susceptibility test results. The software is available from the World Health Organization website: www.who.int/drugresistance/whonetsoftware, and is available in 20 languages.
Objectives of the software include:
· enhancing the local use of laboratory data for guiding therapy, assisting infection control, characterizing resistance epidemiology and identifying laboratory testing errors
· promoting collaboration in surveillance activities through the exchange of data
WHONET can be used for manual data entry, especially in laboratories without an existing computer system for microbiology data. For laboratories which do have systems for managing their data, the BacLink software is a valuable tool which facilitates the extraction and conversion of data from a number of different sources into WHONET, avoiding the need to re-enter results. BacLink can convert data from a number of common commercial database and spreadsheet softwares, commercial susceptibility test instruments, and hospital and laboratory information systems. BacLink, available free of charge from WHO, downloads and installs automatically along with the WHONET software.
WHONET WITH BD EpiCenter™ and BD PHOENIX™
The purpose of this document is to guide users through the process of exporting identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test (AST) data from the BD EpiCenterTM, for import into WHONET. The ID/AST results are generated by the BD Phoenix™ instrument which is connected to the BD EpiCenter™ data management system.
The instructions are divided into four parts:
1. Downloading and installing WHONET and BacLink
2. Exporting data from BD EpiCenterTM
3. Converting data with BacLink
4. Getting started with WHONET
The frequency of data conversions depends on the local data analysis needs and interests. Many laboratories find that a weekly or monthly download is adequate for their infection control and quality assurance purposes, while less frequent analysis may be adequate if the principal use of the data is in following trends in resistance and guiding treatment recommendations.
PART 1. DOWNLOADING AND INSTALLING WHONET AND BacLink
The WHONET and BacLink softwares are available free-of-charge from the World Health Organization website: www.who.int/drugresistance/whonetsoftware
Create a WHONET account and download the latest WHONET setup file.
Double-click the setup file, and select “Run” and follow the installation instructions. This process will install both the WHONET and BacLink softwares by default into the c:\whonet5 folder When you complete the installation you will see icons for WHONET and BacLink on your desktop. Manuals for both softwares can be found in c:\whonet5\docs.
PART 2. EXPORTING DATA FROM BD EPICENTERTM
The BD EpiCenterTM is clinical data management software which allows the export of BD PhoenixTM AST results to WHONET. BD EpiCenterTM software version 6.60 or above is required for this process to work.
BD EpiCenterTM data export
- Launch BD EpiCenterTM (V6.60 or above) and log in.
- Select the “DataView” reporting module from Toolbar.
![]()
![]()
- Select the predefined data filter in the following location “Predefinedà3-WHONET Data ExportàWHONET Data Export” and press “Run”.
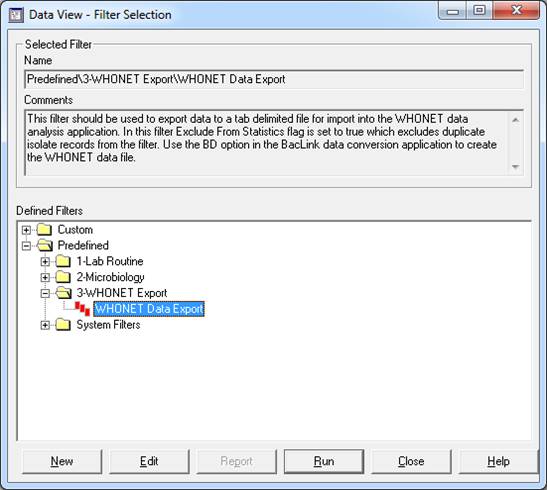
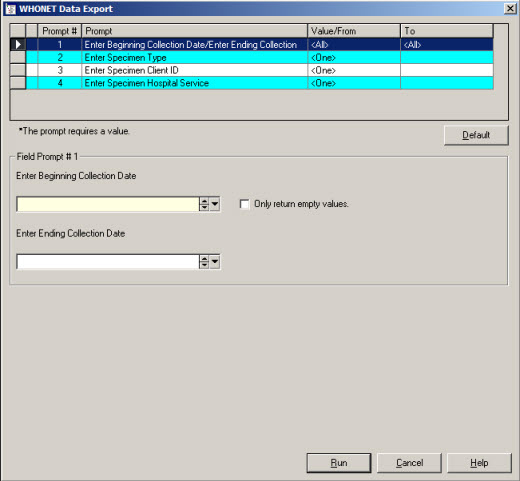
- Enter the appropriate filter criteria to limit the data returned, and press “Run”.
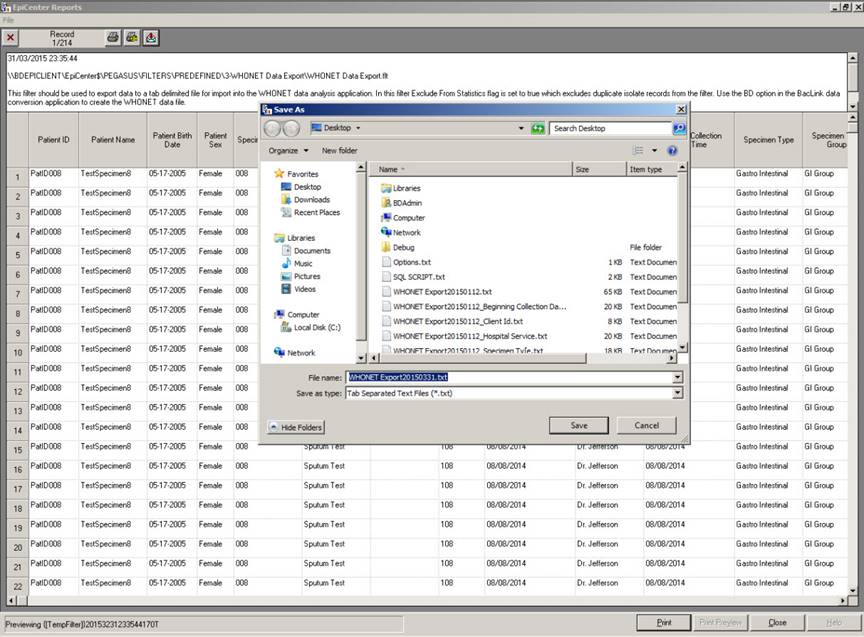
- When the result data has been displayed, click the “Print Preview” option and then select the option to export data to Tab separated text file. File name and export file location will be suggested but can be modified before saving.
For more assistance, refer to the BD EpiCenterTM online help.
PART 3. CONVERTING THE FILE WITH BacLink
Now that you have created a data file with the desired data, BacLink can be used to convert this export file to the WHONET file format. The instructions below are a quick guide.
Start the BacLink program by double-clicking on the BacLink shortcut icon installed on your desktop. The BacLink program screen appears.
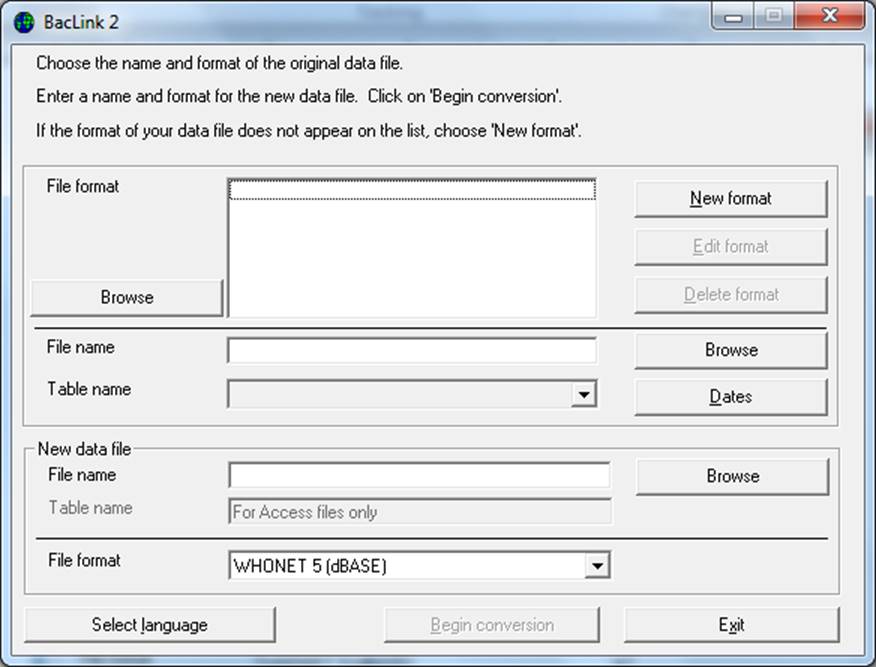
1. Configuring BacLink
The first time BacLink is used, choose the kind of data file you would like to import, as well as the name and a code for your laboratory.
Click on the New Format button. The File Format screen opens.
From the drop down box, select the Country: for example, United States.
Enter the Laboratory Name – the name of your laboratory, for example Boston General Hospital. If data could be imported from a number of different sources you may wish to indicate this in the laboratory name, for example Boston General Hospital (Phoenix).
Enter up to three characters for the Laboratory Code, for example BGH. The laboratory code entered will be used by BacLink and WHONET as the default file extension for your WHONET data files.
Click on the File Structure button, and the below screen will appear. Set the selections as follows:
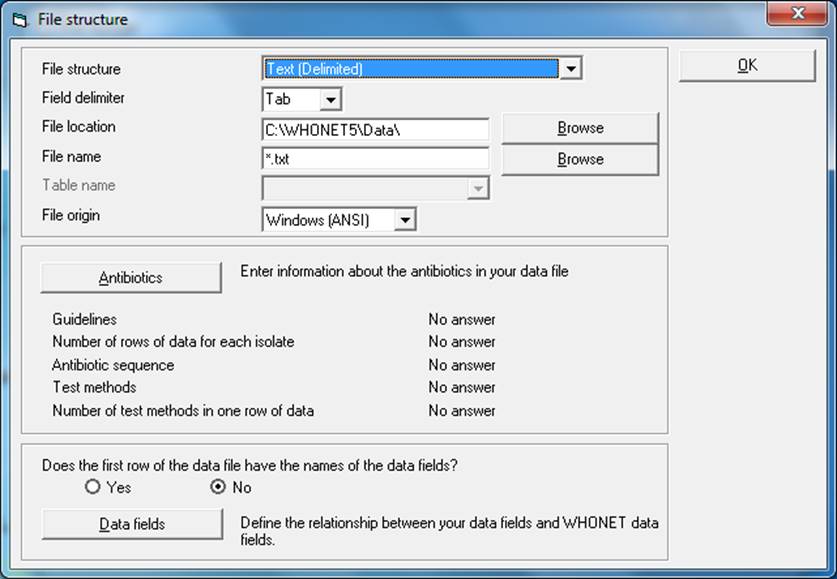
File Structure – BD EpiCenter
File Location – Indicate the folder where the WHONET files will be saved. c:\whonet5\data is the default location suggested by BacLink, but any convenient location can be used. In many institutions, data files are placed in a folder on a central server.
File Name – *.txt
File Origin – Windows (ANSI)
Click on the OK button.
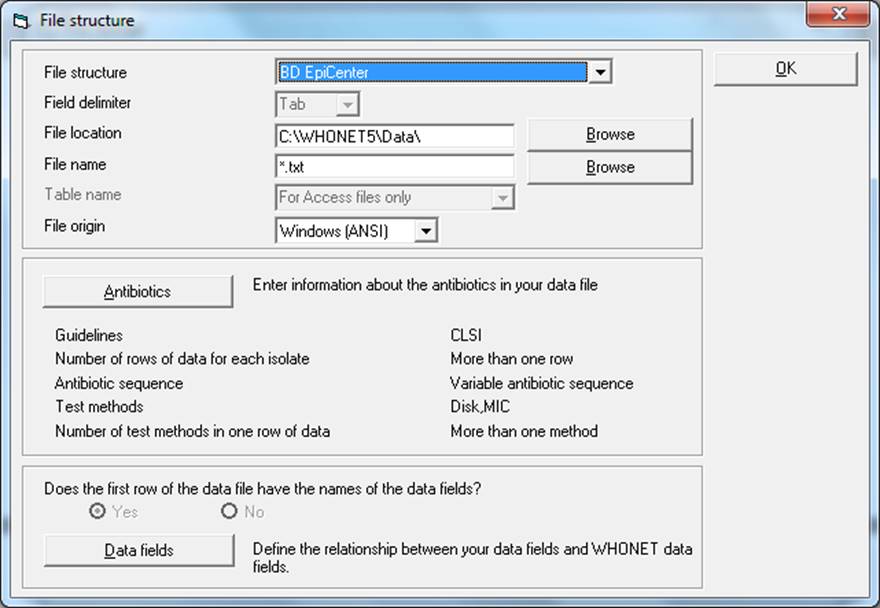
Though not required, you may wish to click on the New data file button. On this screen, you can indicate the default data File location for your new WHONET files. You can indicate the name of the WHONET file that you will create, though it is generally more convenient to give a file name later, just before a file conversion, and not here on this screen. The default WHONET file name will have the three-letter laboratory code as the file extension.
Click on the OK button.
Click on Save. Give a name to the BacLink configuration file, which will save the above-indicated user selections, for example “bgh.cfg”. You may give any valid Windows file name. BacLink will add “.cfg” as a file extension to indicate to BacLink that this is a configuration file.
Click on Exit. This will return you to the main BacLink screen. Your newly defined file format will appear on the list of formats available to you.
2. Converting data with BacLink
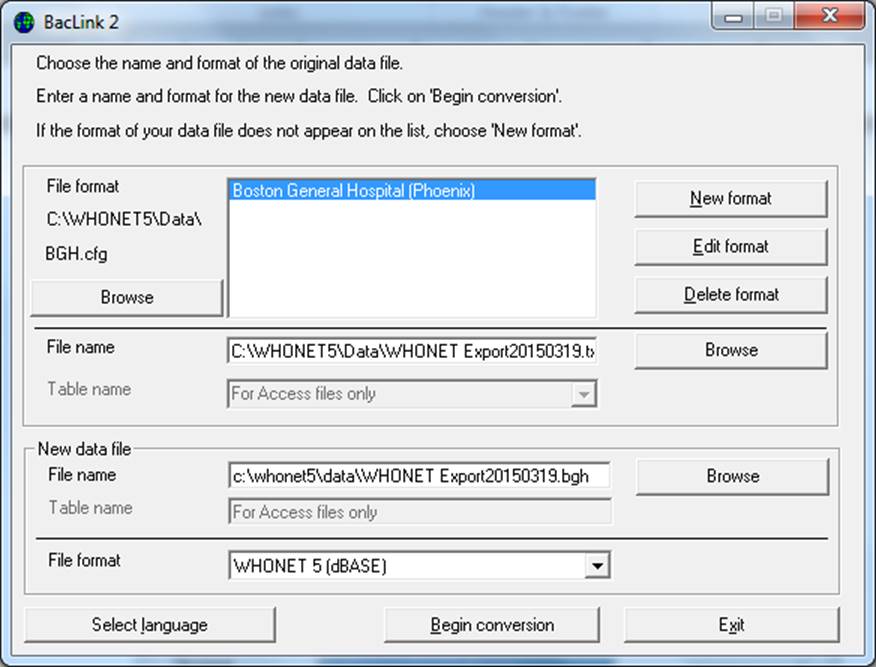
Original data file
From the main BacLink screen, click on the File Format configured in the previous step. For “File name”, browse and select the file to be converted. Example c:\whonet5\data\WHONET Export20150319.txt.
New data file
Enter a name for the new WHONET data file that you wish to create with your converted data. Example: c:\whonet5\data\ WHONET Export20150319.xxx, where ‘xxx’ refers to your three-letter laboratory code. Your screen should look similar to the following:
Click on Begin Conversion. BacLink begins converting the selected Tab delimited text file to a WHONET 5 file. BacLink will display the first three isolates to permit a visual inspection of the accuracy of the conversion. The information from your data file, as read by BacLink, appears to the left of the screen. The information which will be saved in the WHONET file appears to the right of the screen. Where appropriate, WHONET will change your codes and formats to those used by WHONET.
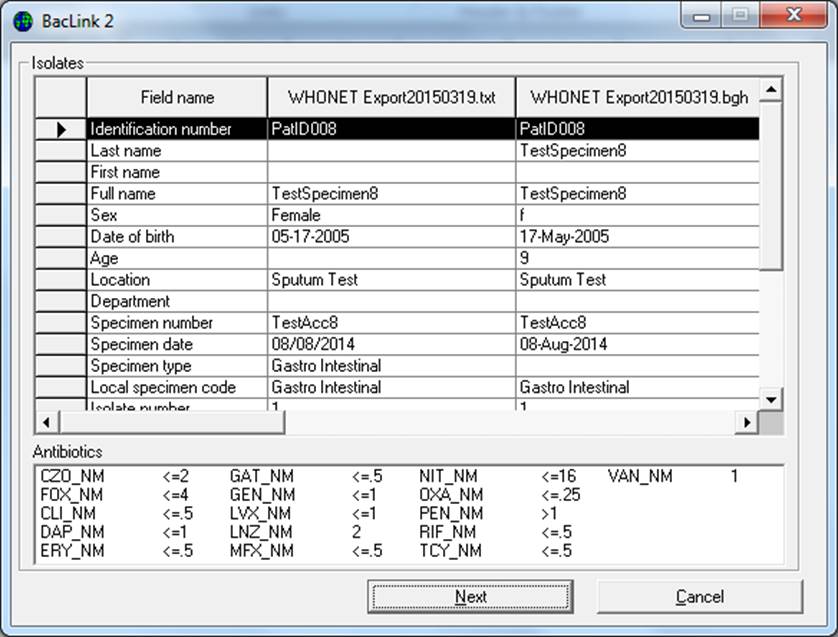
If you notice any discrepancies or errors in the field mappings, you may correct these from the main BacLink screen using “Edit format”. Click “Next” to advance through the first three isolates. BacLink will then continue until the file is completely converted.
If BacLink does not understand some of the data codes in your file, the program asks whether you would like to define the unrecognized codes. If you answer Yes, you will be shown a list of the various organism, antibiotic, specimen type, location, gender, and test result codes that could not be understand. Click on a variable of interest, such as “Organism”, and click Define codes.
You will subsequently be shown a list of each of the unrecognized code. Select a code and click Define code. For most variables (except Location), you will be asked to select the matching or closest term from a list of WHONET codes. For Location you will have the option of defining the patient department and type (inpatient, outpatient, ICU, etc.). Continue defining codes until you have defined all, or at least the most important and frequent, data elements. When finished click “OK”, then “OK” again to return to the main BacLink screen.
If you have defined some additional codes, you should then convert the same file a second time in order to include the new code matchings in the converted data file. When finished with BacLink, click Exit.
PART 4. GETTING STARTED WITH WHONET
Now that you have created a valid WHONET file using BacLink and your BD EpiCenterTM data, you can proceed to WHONET. For details on the use of WHONET, consult the manual WHONET 5.0 whonet5manual.doc, as well as available update pages describing the enhancements of further versions of the software.
1. Creating a laboratory configuration
To begin using WHONET, you must first create a “Laboratory configuration” with descriptive information about your laboratory -- antibiotics, breakpoints, patient locations, etc. For laboratories not using BacLink, this is typically done with a feature called New laboratory. However, for users of BacLink, there is a shortcut available called Create a laboratory from a data file.
Double-click on the WHONET icon. You will be shown a list of WHONET laboratories defined on your computer (with the default installation, you will see a single laboratory – “USA Test Hospital”). To access the aforementioned shortcut, click on Cancel. Then click File from the main WHONET menu, and then the option Create a laboratory from a data file.
You will be asked to indicate your country, laboratory name, and laboratory code. Enter the responses using the same country and laboratory code which you selected in BacLink.
You will then be requested to select a valid WHONET data file. Search for and select the file created above using BacLink. Then click OK. At this point, WHONET will scan the contents of this file – antibiotics, location codes, etc. – and create a valid WHONET laboratory configuration. When requested, you can click Yes if you want to review the details of the configuration. Otherwise, click No, and continue with Data analysis.
Note: After creating the configuration utilizing the here-described shortcut, further edits, such as any modifications to the antibiotic breakpoints, can be done with Modify laboratory.
2. Using WHONET
Once you have defined a laboratory configuration, it will appear in the list of laboratories when you enter WHONET. Click on your laboratory name. For data entry or data analysis options, click on Open laboratory. If you wish to modify the laboratory information in the configuration, click on Modify laboratory. For use of the WHONET analysis features, explore the screen display and/or consult the manual.